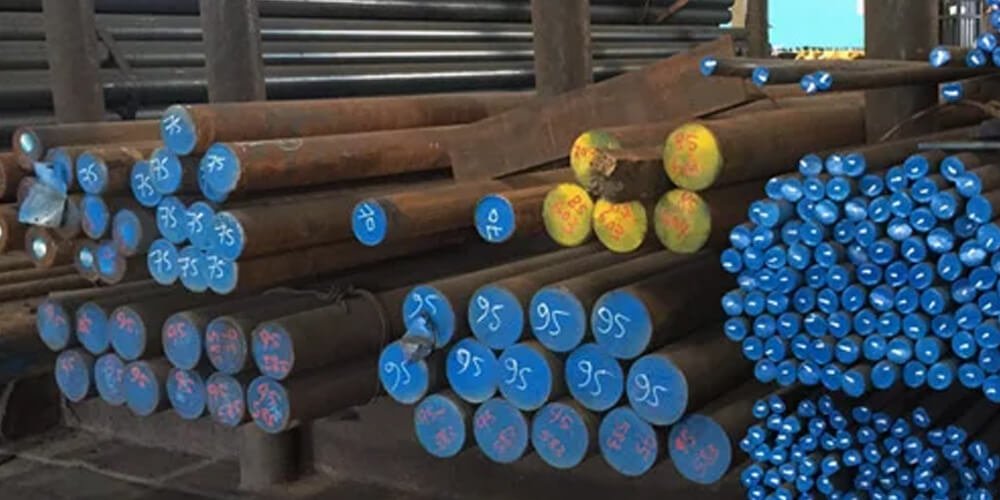
Best EN9 Carbon Steel Manufacturers & Suppliers in Mumbai – High Quality Carbon Steel Round Supply
Looking for trusted EN9 Carbon Steel Round Bar Manufacturers & Suppliers in Mumbai ? We Titan Steel, Mumbai provide durable, precision-engineered carbon steel round bars for construction, industrial, and engineering needs. Get reliable quality, competitive prices, and timely delivery from leading suppliers in Mumbai.
EN9 Grade Introduction:
EN9 carbon steel is a medium carbon steel grade, typically supplied in the as-rolled condition. It is known for its ability to be flame or induction hardened, achieving a high surface hardness while maintaining good wear resistance. EN9 steel can be supplied as round bars, cut to length, or flame cut steel plates, and can be normalized and precision ground to meet customer requirements.
EN9 Grade Application:
EN9 steel is widely used in general engineering applications due to its strength and durability. Typical uses include:
- Shafts
- Axes
- Knives
- Bushes
- Crankshafts
- Screws
- Sickles
- Woodworking drills
- Hammers
EN9 Equivalent Grades:
| Standard | Equivalent Grades |
|---|---|
| BS 970:1991 | 070M55 |
| BS 970:1955 | EN9 |
| AISI/SAE | 1055 |
| Werkstoff | 1.0535 |
Additional Grades Available:
In addition to EN9, we supply a range of steel grades, including EN1A, EN3B, EN8, EN24, EN31, and alloy steels like 42CrMo4, D2, H13, and more.
EN9 Chemical Composition:
| Element | C | Si | Mn | P (Max) | S | Cr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content % | 0.50-0.60 | 0.4 Max | 0.50-0.80 | 0.035 Max | 0.015-0.035 | 0.30 Max |
EN9 Mechanical Properties:
| Condition | N | R | S | T |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ruling Section (mm) | 254 | 100 | 65 | 20 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 600-700 | 690-850 | 770-930 | 850-1000 |
| Yield Strength (MPa) | ≥310 | ≥415 | ≥480 | ≥570 |
| Elongation (%) | 13% | 14% | 14% | 12% |
| Hardness (HBW) | 201-255 | 201-255 | 223-277 | 248-302 |
EN9 Hardness:
EN9 can achieve Brinell hardness levels in the range of 201-302 HBW, depending on the condition and heat treatment.
EN9 Heat Treatment:
Heat treatment parameters such as heating rate, cooling rate, and soaking time will depend on the size and shape of the EN9 steel component. Factors such as the type of furnace, quenching medium, and workpiece transfer methods also play an important role.
EN9 Hardening:
For hardening, heat the EN9 steel slowly to 820-840°C and allow the steel to be thoroughly heated. Quenching can be done in oil, brine, or water.
EN9 Tempering:
After quenching, tempering should be performed immediately while the component is still warm. Reheat to the tempering temperature (usually 550-660°C), soak for one hour per 25 mm of thickness, and allow to cool in air.
EN9 Physical Properties:
EN9 possesses good strength, ductility, and wear resistance, making it ideal for demanding applications.
EN9 Thermal Properties:
EN9 steel can withstand moderate thermal conditions but will require tempering after hardening to maintain stability in variable temperatures.
EN9 Forging Properties:
Preheat the EN9 steel carefully before raising the temperature to 1100°C for forging. Avoid forging below 850°C and allow the material to cool slowly, preferably in a furnace, for optimal results.
EN9 Stress Relieving:
Stress relieving is recommended after heavy machining to minimize internal stresses that can affect performance during use.
EN9 Normalizing:
The normalizing temperature for EN9 is typically in the range of 820-880°C, followed by air cooling to refine the grain structure and enhance machinability.
EN9 Annealing:
Annealing involves heating the EN9 steel to 680-710°C, soaking thoroughly, and cooling slowly within the furnace to achieve a softer, more machinable state.
EN9 Density:
EN9 steel has a typical density, providing good mechanical properties and durability for industrial applications.
EN9 Machinability:
EN9 steel is moderately machinable. It is suitable for various machining operations, including turning, milling, and drilling.
EN9 Welding:
EN9 can be welded using standard techniques, but preheating and post-weld heat treatment may be necessary to prevent cracking and maintain material strength.
Titan Steel & Engineers Related Products:
Carbon Steel, Alloy Steel, Bright Steel, Spring Steel, Die Steel & Tool Steel, Special Alloy Steel
For Visit us Maps
Supply Cities
- Mumbai
- Ahmedabad
- Amaravathi
- Ambattur
- Bangalore
- Belgaum
- Chennai
- Chittoor
- Coimbatore
- Dindigul
- Mysore
- Nellore
- Hyderabad
- Kochi
- Mangalore
- Tirupur
- Tuticorin
- Madurai
- Andhra Pradesh
- Karnataka
- Puducherry
- Kerala
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Visakhapatnam
- Kochi
- Kerala
- Hubli-Dharwad
- Karnataka